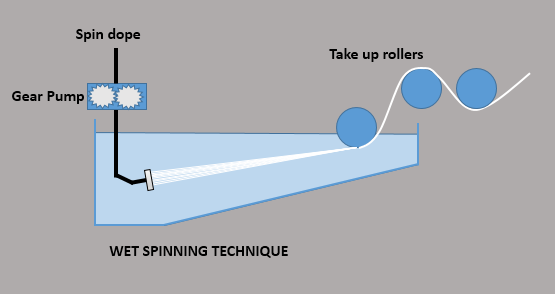
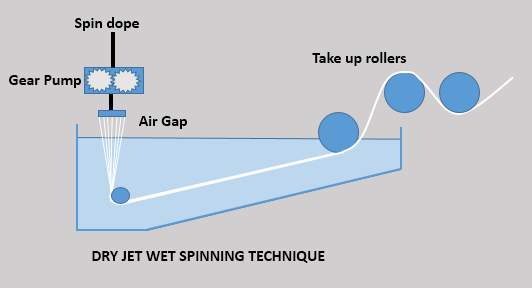
COMPOSITIONAL ANALYSIS
Compositional analysis methods can be used to determine the components of an unknown material, to confirm the identity of a suspect material and to identify differences between similar materials. Chemical composition analysis requires the application of a combination of analytical methods in order to achieve a full picture of the chemical structures and concentrations of the components in a sample. Our chemical analysis scientists have considerable expertise in determining the chemical composition of a sample, trace analysis, reverse engineering, elemental analysis, concentration or purity of sample and advanced research support. We regularly develop and optimize (and validate, if necessary) analytical methods to make them suitable for our requirements and the industry sector which approaches us.
Technique Name:
- High Pressure Liquid Chromatography (HPLC)
- Gas Chromatography (GC)
- Elemental analysis
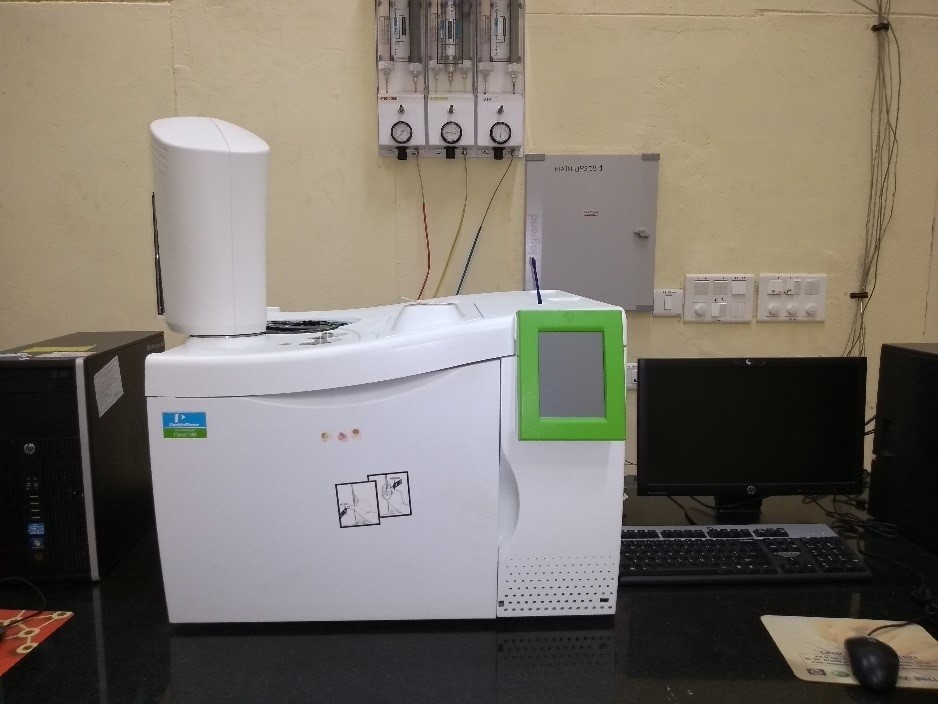
- High Pressure Liquid Chromatography (HPLC)
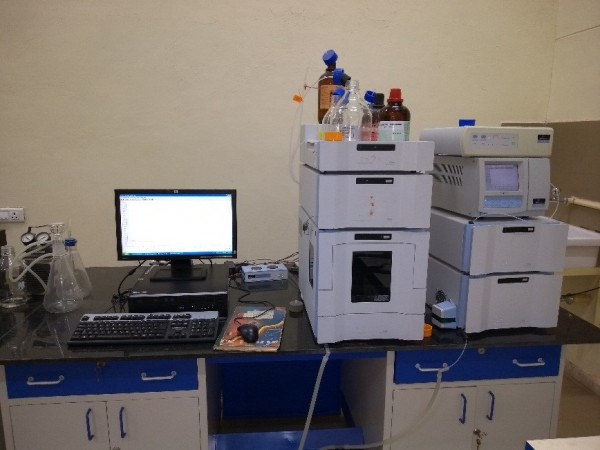

The main purposes for using HPLC are for identifying, quantifying and purifying the individual components of the mixture. HPLC is a form of liquid chromatography used to separate compounds that are dissolved in solution. The instruments used at CCFP is “Flexar LC” by PerkinElmer which consist of a reservoir of mobile phase, a pump, an injector, a separation column, UV spectrometer detector, an oven and an auto sampler and computer for data acquisition.
Facilities where this technique is used:
At CCFP this method is used to determine the composition of the co-monomer solution prepared prior to polymerization. This is also used to determine the composition of some critical components in the resin systems.
- Gas Chromatography (GC)
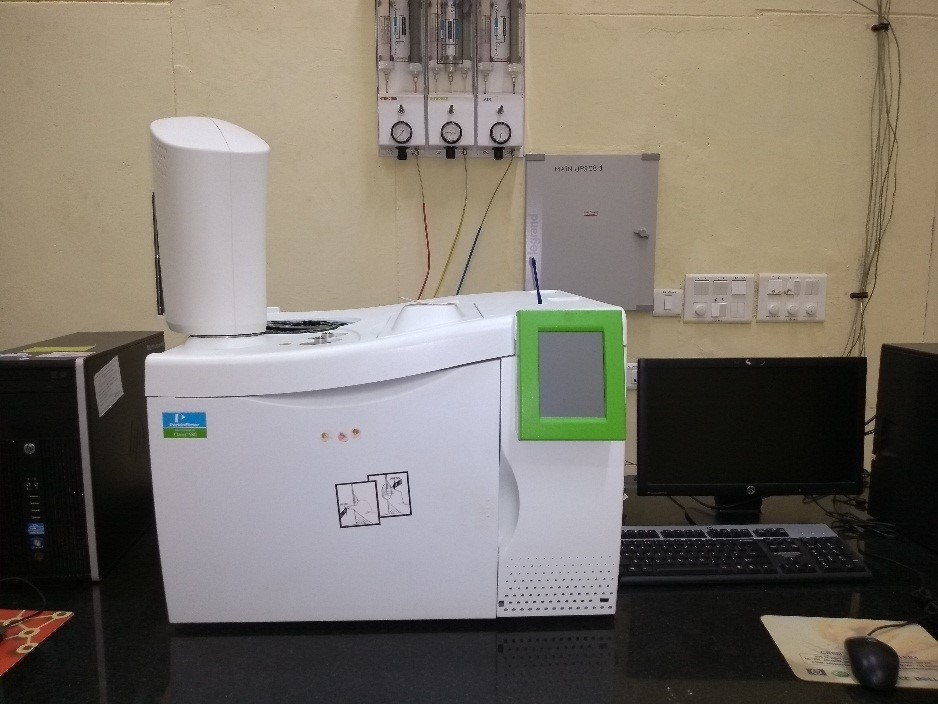
A gas chromatograph (GC) is an analytical instrument that measures the content of various components as well as the purity of a sample. The sample solution injected into the instrument enters a gas stream which transports the sample into a separation tube known as the "column." (Helium or nitrogen is used as the carrier gas.) The various components are separated inside the column. The detector measures the quantity of the components that exit the column. The GC at CCFP is “Clarus 580” PerkinElmer make and it consists of column (for both polar and non-polar samples), thermal conductivity detector, auto sampler, oven, computer integrator.

Facilities where this technique is used:
This method is used to check the purity of the raw materials used in polymerization as well as spinning. It is also used to check the co-monomer composition which is prepared during the polymerizations process.
- Elemental analysis
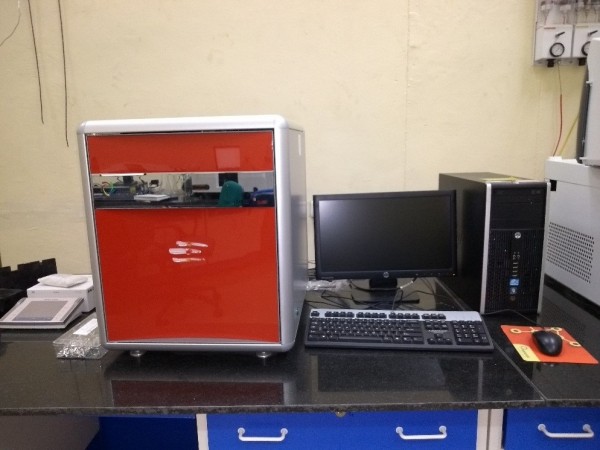
Elemental analysis on carbon, hydrogen and nitrogen is the most essential - and in many cases the only - investigation performed to characterize and/or prove the elemental composition of an organic sample. In this technique, a sample is burned in combustion tube in an excess of oxygen and various traps (reduction tubes), collecting the combustion products: carbon dioxide, water, and nitric oxide. The masses of these combustion products can be used to calculate the composition of the unknown sample. High purity helium gas acts as carrier gas. At CCFP we have “Elementar Vario Micro cube” elemental analyser which is capable of simultaneous determination of sulfur along with CHN in the same measurement run. The instrument can operate both in CHNS mode as well as O mode (oxygen can be analysed separately). With unique combination of both static and dynamic combustion, the CHN/O/S instrument can combust the widest range of sample type, from volatiles to refractories. Fully automated. Rapid analysis for high productivity - analysis time of less than 10 minutes per sample. Stable thermal conductivity detector provides linear response with superior precision and accuracy. Horizontal sample injection removes interfering residue between each sample run. Mettler XP6 ultramicrobalance is used to weigh the material

Facilities where this technique is used: Fiber spinning facility (F2), Fiber heat treatment facility (F3).
The elemental composition of the precursor fiber (Special acrylic fiber) as well as the various heat treated fiber (Stabilized, pre-carbonized and carbonized) are determined to know the mass loss as well as the oxygen pick up at various stages of heating during stabilization of the fiber. The elemental composition of polymers, lignin and other fibers (glass, aramid fiber) have also been determined.

 English
English हिन्दी
हिन्दी