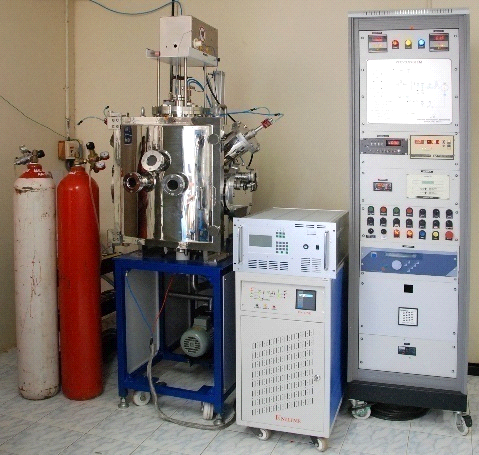
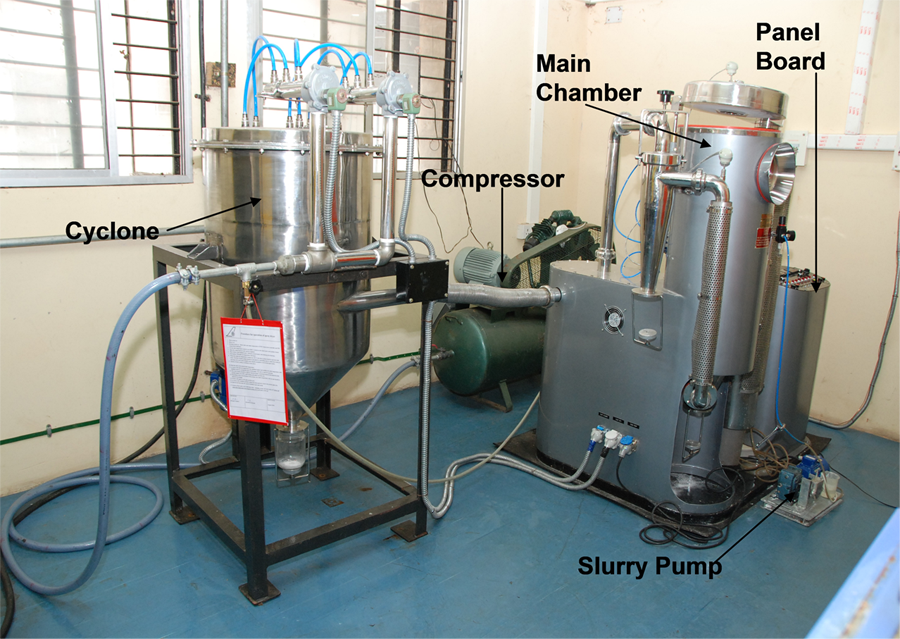
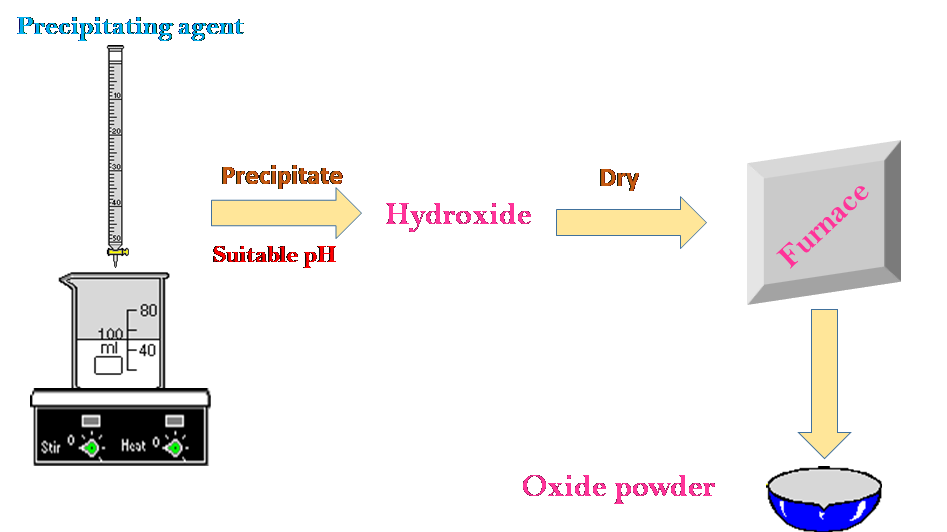
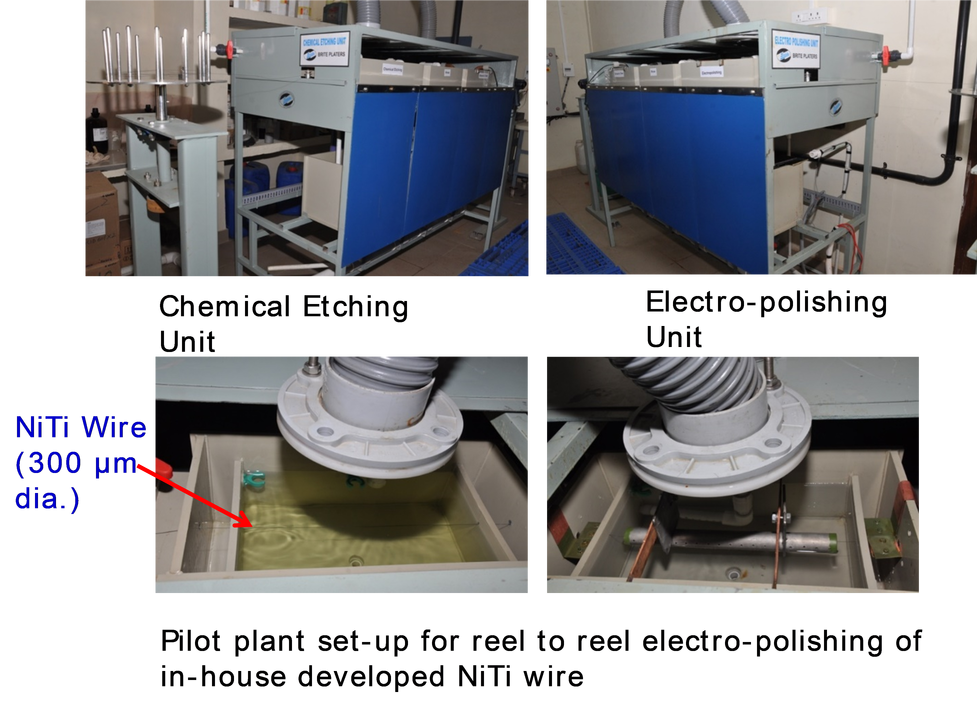
Hot-filament chemical vapor deposition
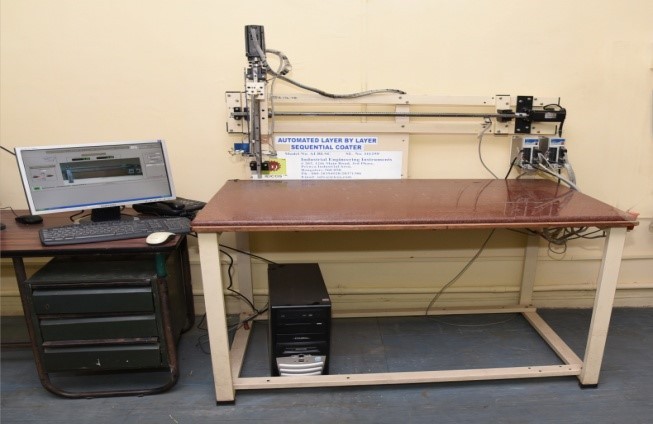
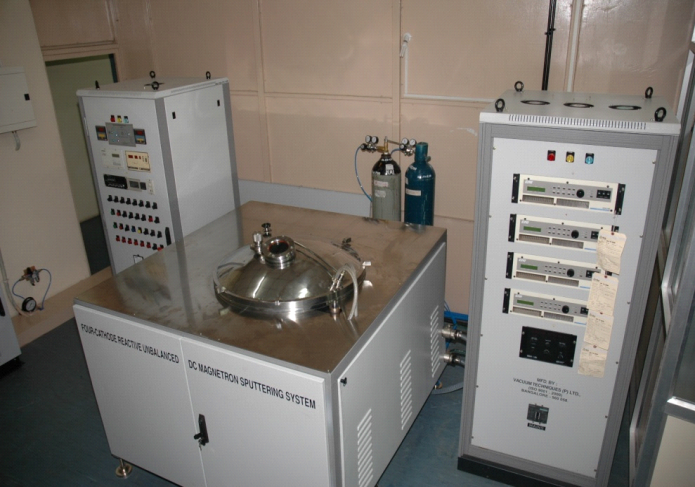
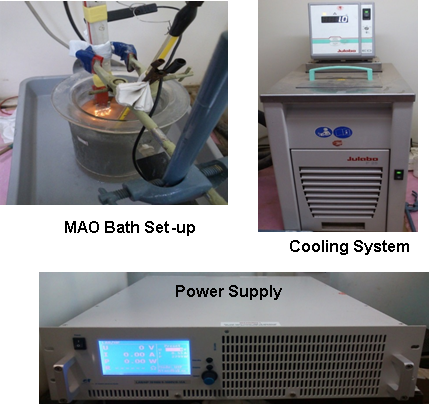
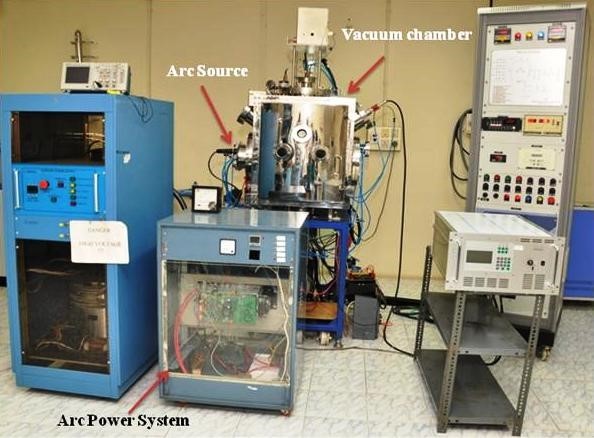
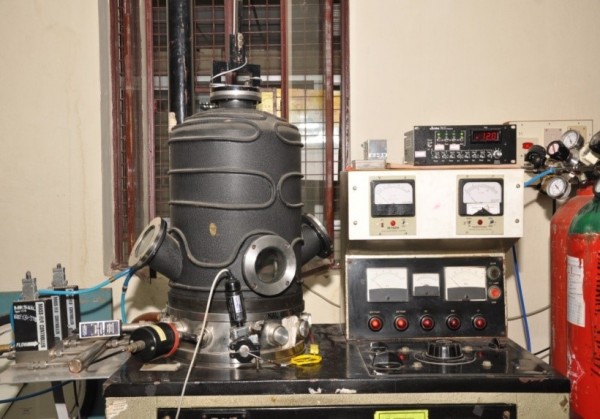
Hot-filament chemical vapor deposition (HFCVD) is a simple and cost effective method which has been used to deposit a variety of materials. In the HFCVD technique, a resistively heated metallic filament (such as tungsten, rhenium or tantalum) is used to thermally/catalytically dissociate the molecules of the source gas to produce the required reactive precursors. Hot-filament CVD is more advantageous when compared to other CVD techniques. Graphene grown by CVD has generated interest due to low cost preparation and large-area deposition capabilities. Using this technique, monolayer, bi-layer and multilayer graphene has been grown on Cu foils (2″X2″) with high uniformity.


 English
English हिन्दी
हिन्दी